Domain Name System Explanation
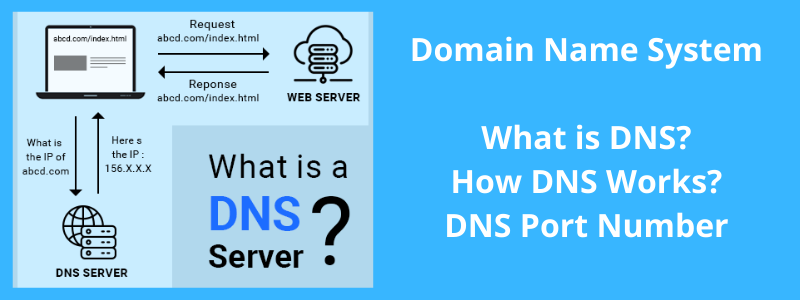
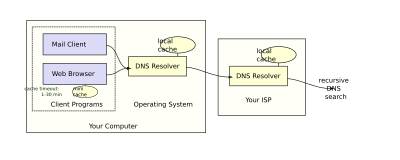
The domain name system dns is a naming database in which internet domain names are located and translated into internet protocol addresses the domain name system maps the name people use to locate a website to the ip address that a computer uses to locate a website.
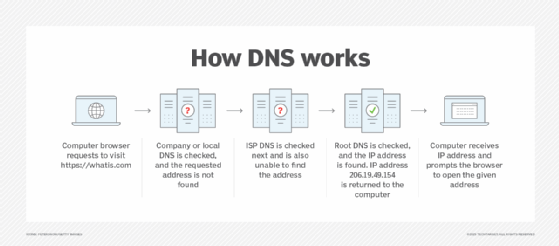
Domain name system explanation. Short for domain name system dns is an internet service that translates domain names to ip addresses domain names are alphabetic and therefore easy to remember but the internet is based on numeric ip addresses so a dns server is required for computers to communicate with one another. Its primary task is to resolve the naming requests. Domain name system dns is a hierarchical naming system built on a distributed database. In simple terms a domain name system dns is a collection of databases that translate hostnames to ip addresses.
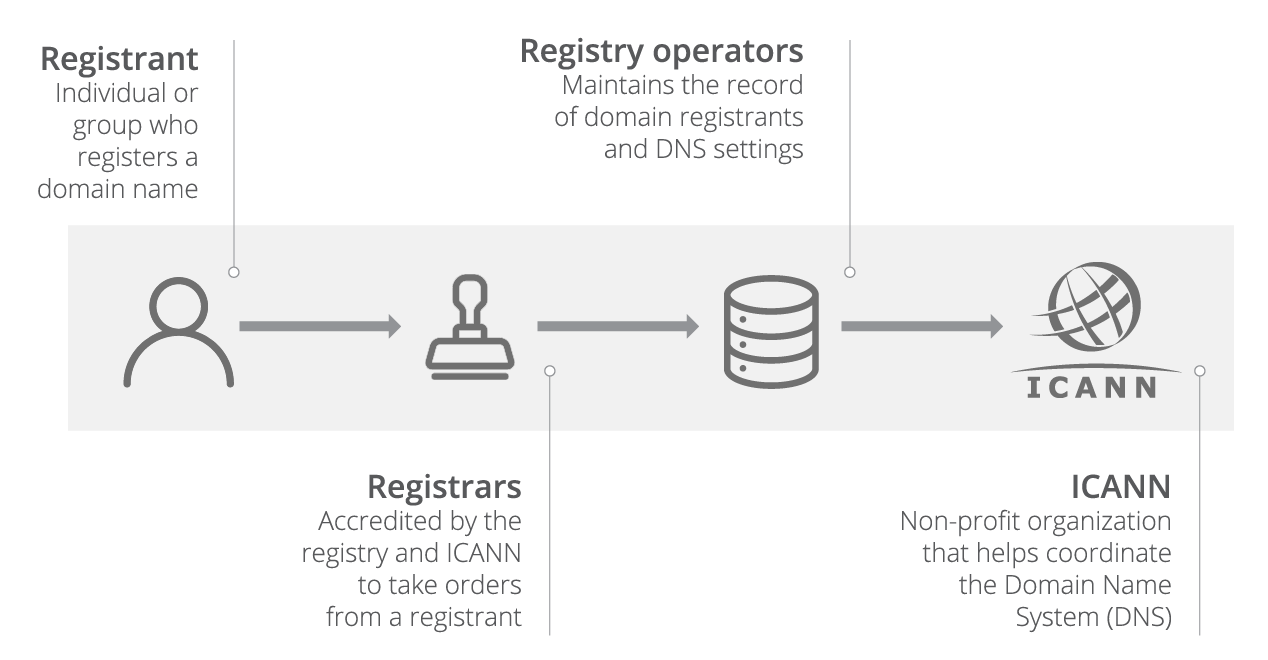
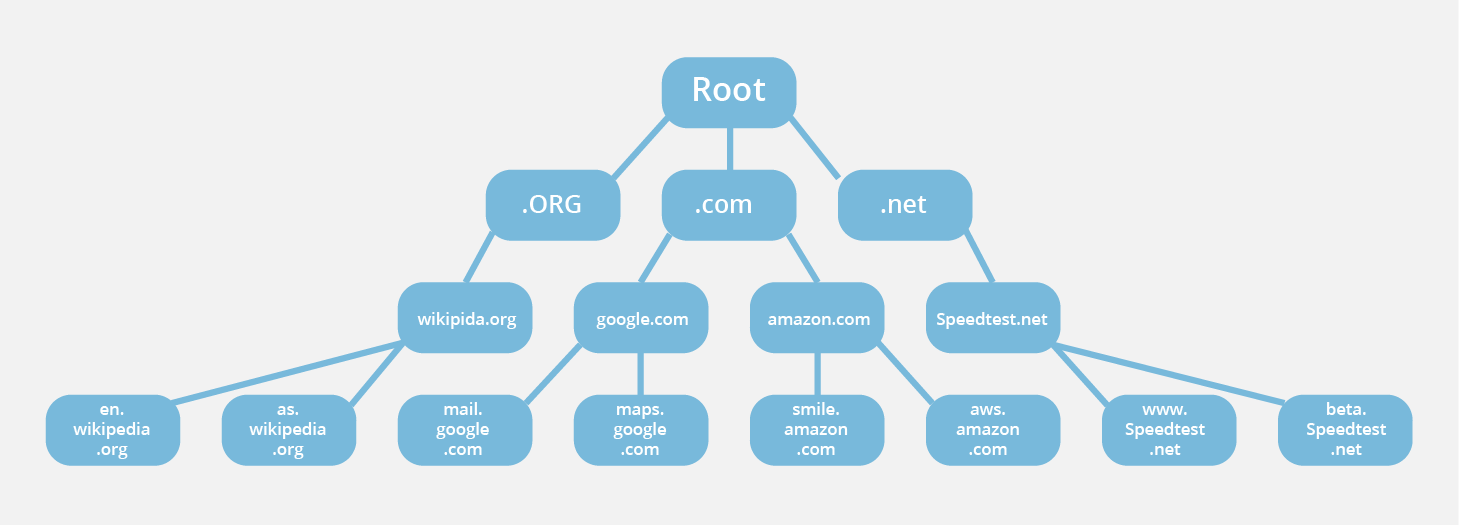
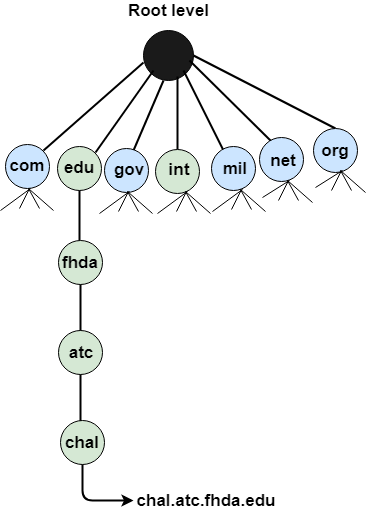
The domain name system dns is the phonebook of the internet. What is the definition of dns. Dns domain name system is a hierarchical nomenclature system that deals with domain name space management. Domain name system domain name server what does it mean.
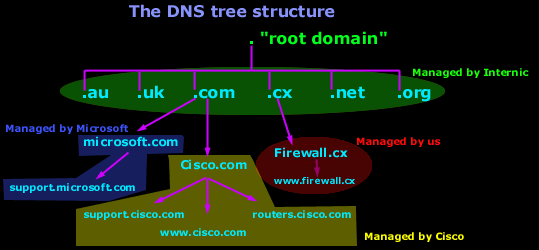
Functions of domain name system. Web browsers interact through internet protocol ip addresses. It translates unfathomable amounts of data into words and phrases in order to provide clear and accurate search results. The domain name system dns is a hierarchical and decentralized naming system for computers services or other resources connected to the internet or a private network.
It is an internet system whose function is to translates alphabetic domain names into ip addresses. This system transforms domain names to ip addresses and makes it possible to assign domain names to groups of internet resources and users regardless of the entities physical location. Well in the simplest definition dns is the term used to describe a system that assigns user friendly domain names to unique ip addresses. The explanation of this function can be by comparison with a telephone information service that has current contact data and provides them when someone requests them.
To bridge the communication gap between computer humans. Most prominently it translates more readily memorized domain names to the numerical ip addresses needed for locating and. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities.