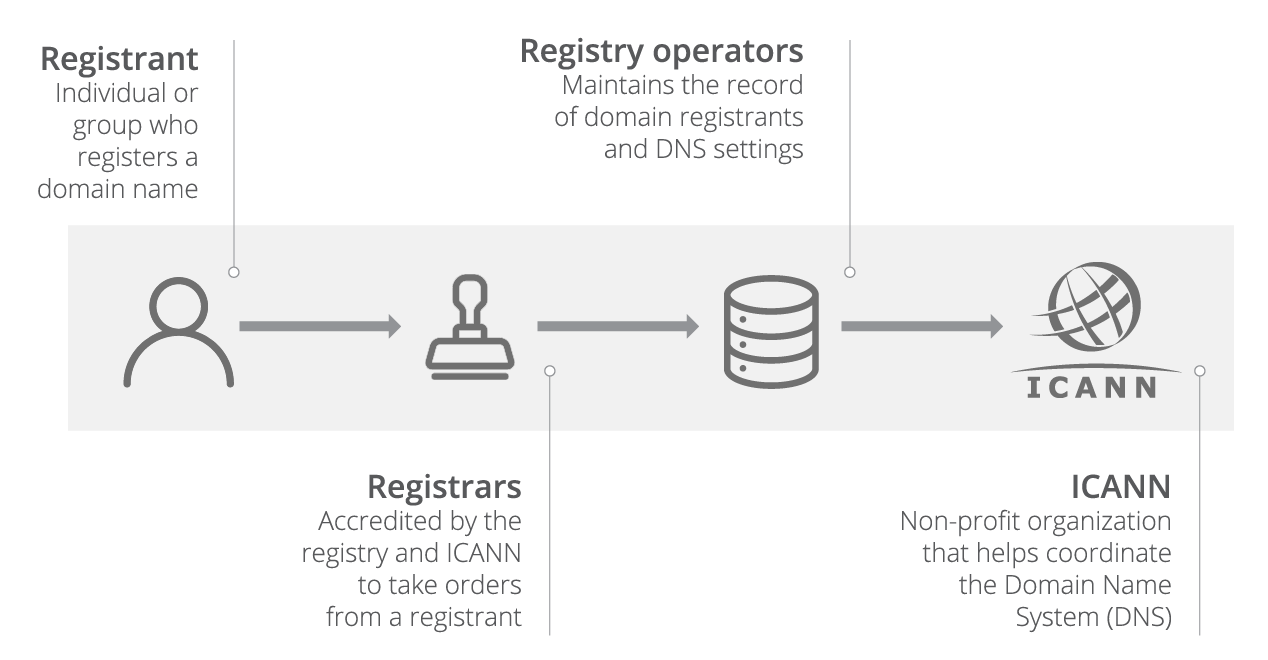
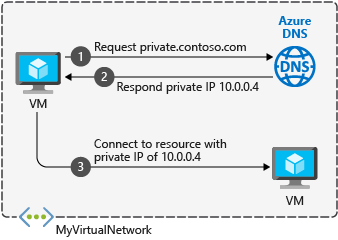
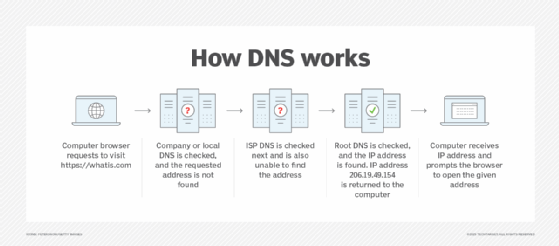
Domain Name System Public Key

Dkim allows the receiver to check that an email claimed to have come from a specific domain was indeed authorized by the owner of that domain.
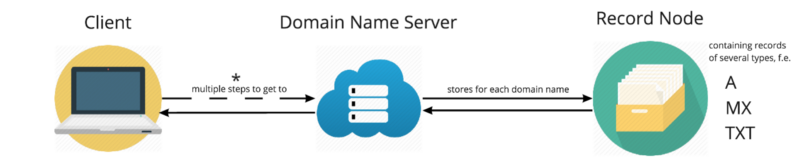
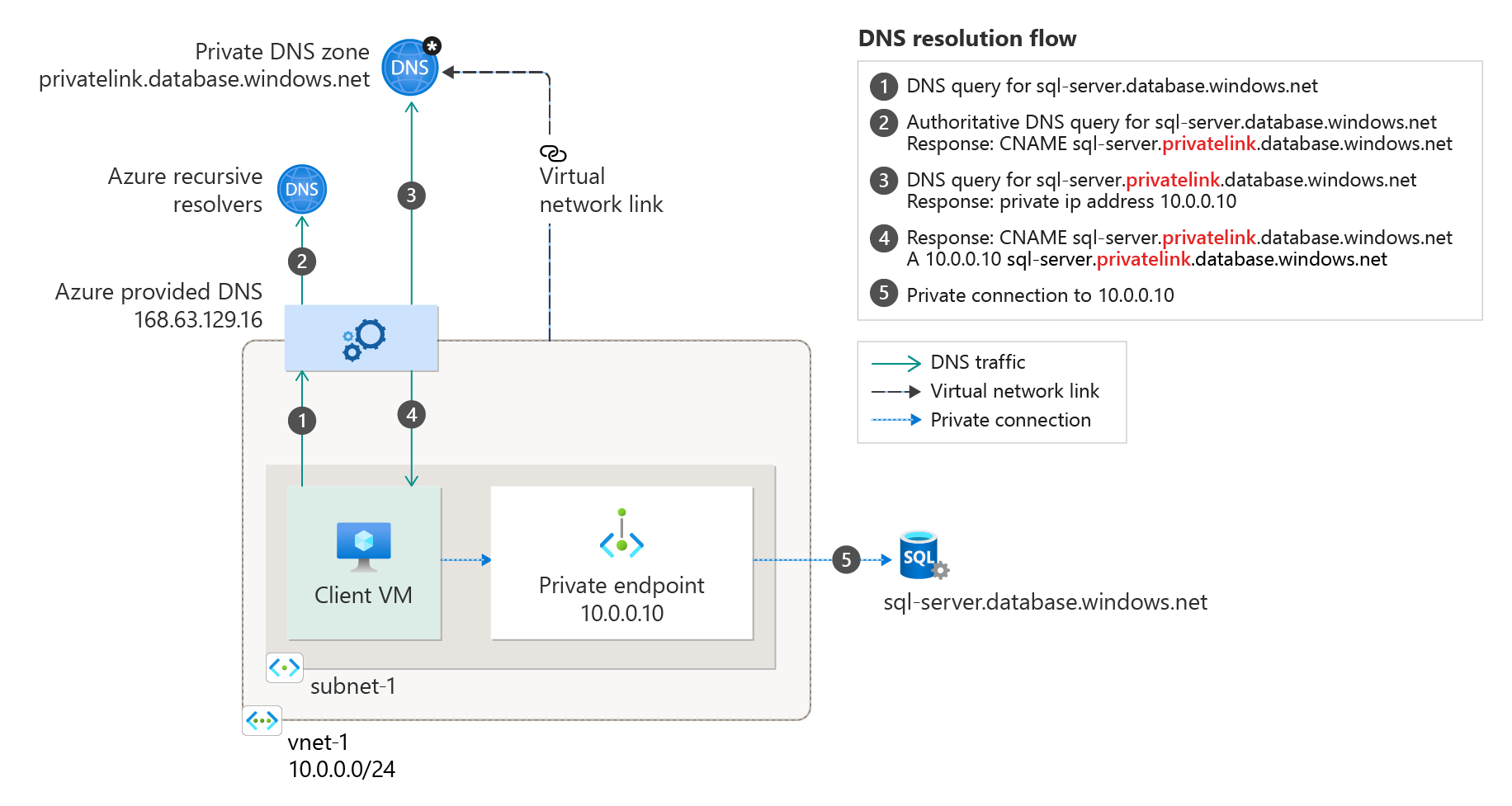
Domain name system public key. It is a set of extensions to dns which provide to dns clients resolvers cryptographic authentication of dns data authenticated denial of existence. In cryptography a public key certificate also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate is an electronic document used to prove the ownership of a public key. The domain name system security extensions dnssec is a suite of internet engineering task force ietf specifications for securing certain kinds of information provided by the domain name system dns as used on internet protocol ip networks. Public key cryptography is a cryptographic technique that enables entities to securely communicate on an insecure public network and reliably verify the identity of an entity via digital signatures.
The domain name system comprises of domain names domain name space name server that have been described below. The ksk rollover can be thought of as changing the locks on a house. The public key is stored and published in the domain name system dns. The certificate includes information about the key information about the identity of its owner called the subject and the digital signature of an entity that has verified the certificate s contents called the issuer.
Any recursive resolver that looks up data in the zone also retrieves the zone s public key. Some of them are generic such as com edu gov net etc while some country level domain names such as au in za. To understand domain name system security extensions dnssec it helps to have a basic understanding of the domain name system dns. A public key infrastructure pki is a system for the creation storage and distribution of digital certificates which are used to verify that a particular public key belongs to a.
Domain name is a symbolic string associated with an ip address. The recipient system can verify this by looking up the sender s public key published in the dns. When an email message is sent the mail server uses the private key to digitally sign it which is a part of the message header. There are several domain names available.