Domain Of A Function Explained

Functions domain and range explained.
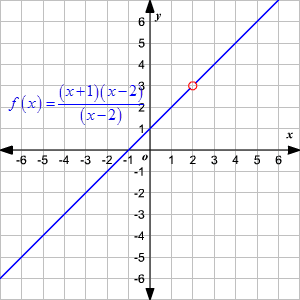
Domain of a function explained. Change the domain and we have a different function. A simple function like f x x 2 can have the domain what goes in of just the counting numbers 1 2 3. Here are the basics that you need to know about each type of function which will be explained in the next section. The domain of a function is the set of all possible inputs for the function.
Domain and range of a function definitions of domain and range domain. In the following tutorial i continue by looking at square root and reciprocal functions. There are also many types of subdomains. So in the following tutorials i introduce you to this concept by looking at linear quadratic root and reciprocal functions.
A domain in the context of networking refers to any group of users workstations devices printers computers and database servers that share different types of data via network resources. A function with a fraction with a variable in the denominator. We can also define special functions whose domains are more limited. For example the domain of f x x is all real numbers and the domain of g x 1 x is all real numbers except for x 0.
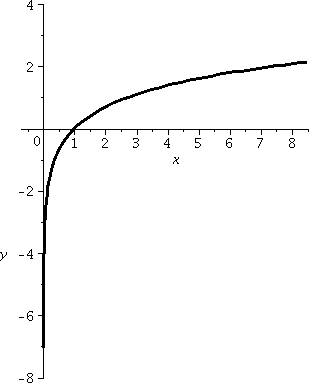
I am often asked what is the domain and range of a function. For this type of function the domain is all real numbers. Finding domain and range from a graph can be accomplished by. The domain of a function is the complete set of possible values of the independent variable.
Domains limit what you can do on your pc. When your computer is part of a domain the domain controller is in charge of what you can do. The domain is the set of all possible x values which will make the function work and will output real y values. Functions assign outputs to inputs.
You shouldn t do this to a work or school pc you don t own of course. In fact the domain is an essential part of the function. In plain english this definition means. When finding the domain remember.
The domain of a function is the collection of all the possible inputs while the range is the collection of all the possible outputs. A domain has a domain controller that governs all basic domain functions and manages network security.