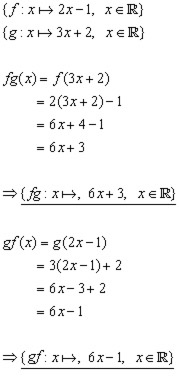Domain Of Composite Functions Rule

Thanks to all of you who support me on patreon.
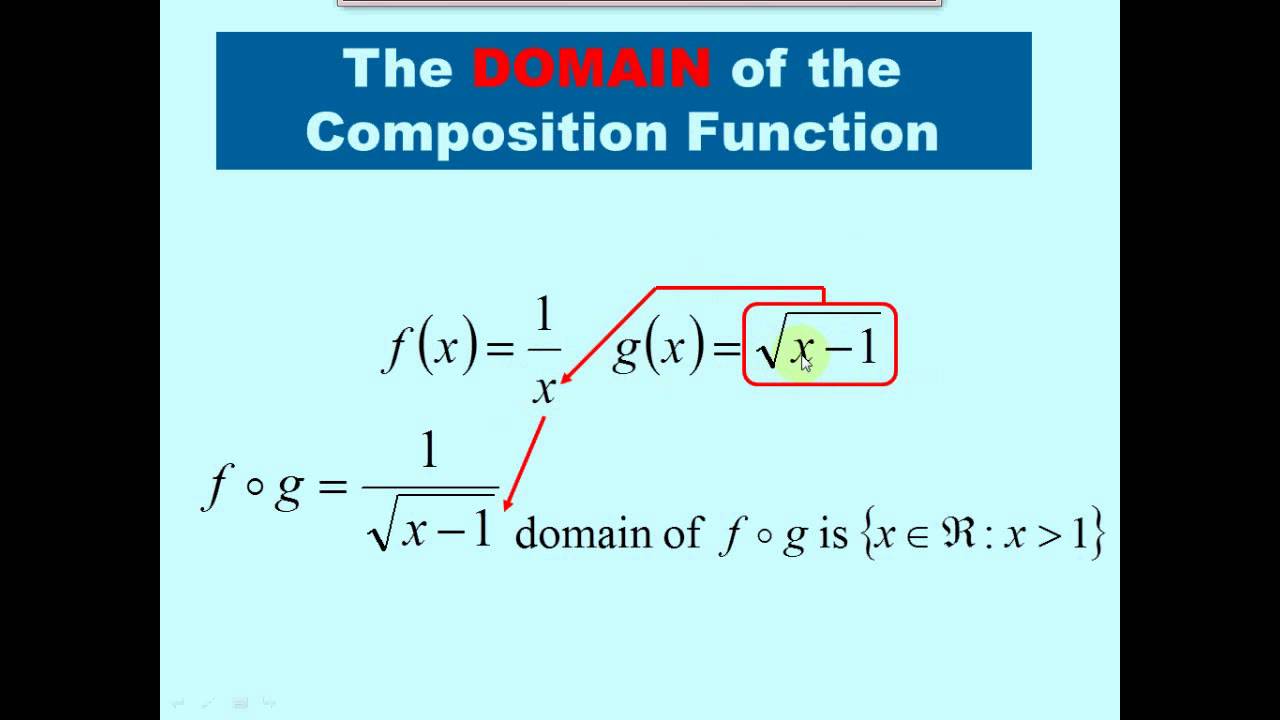
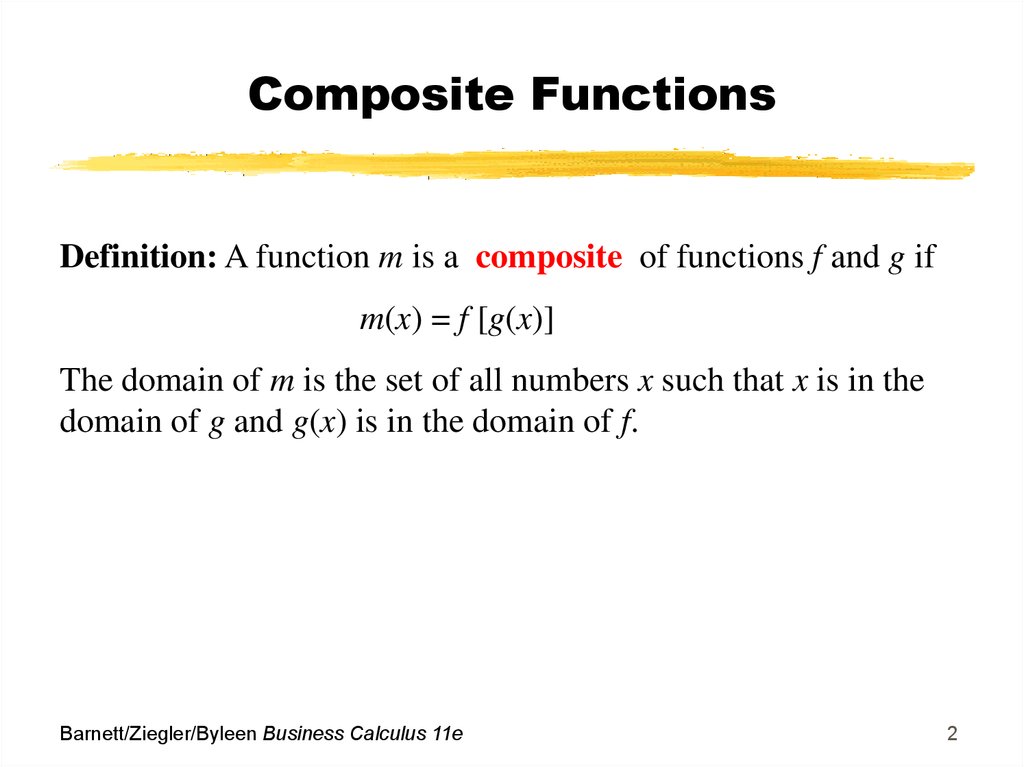
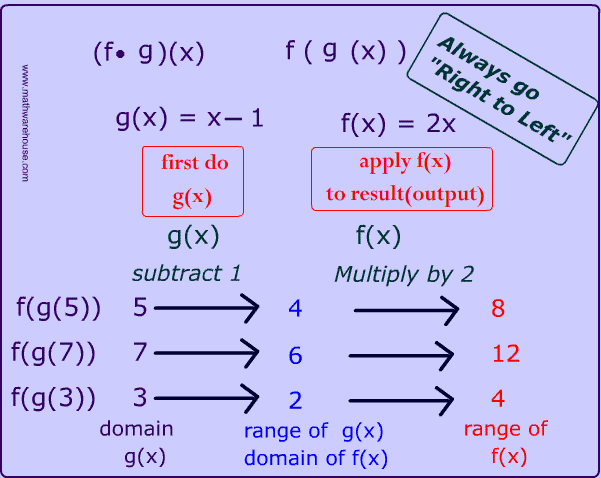
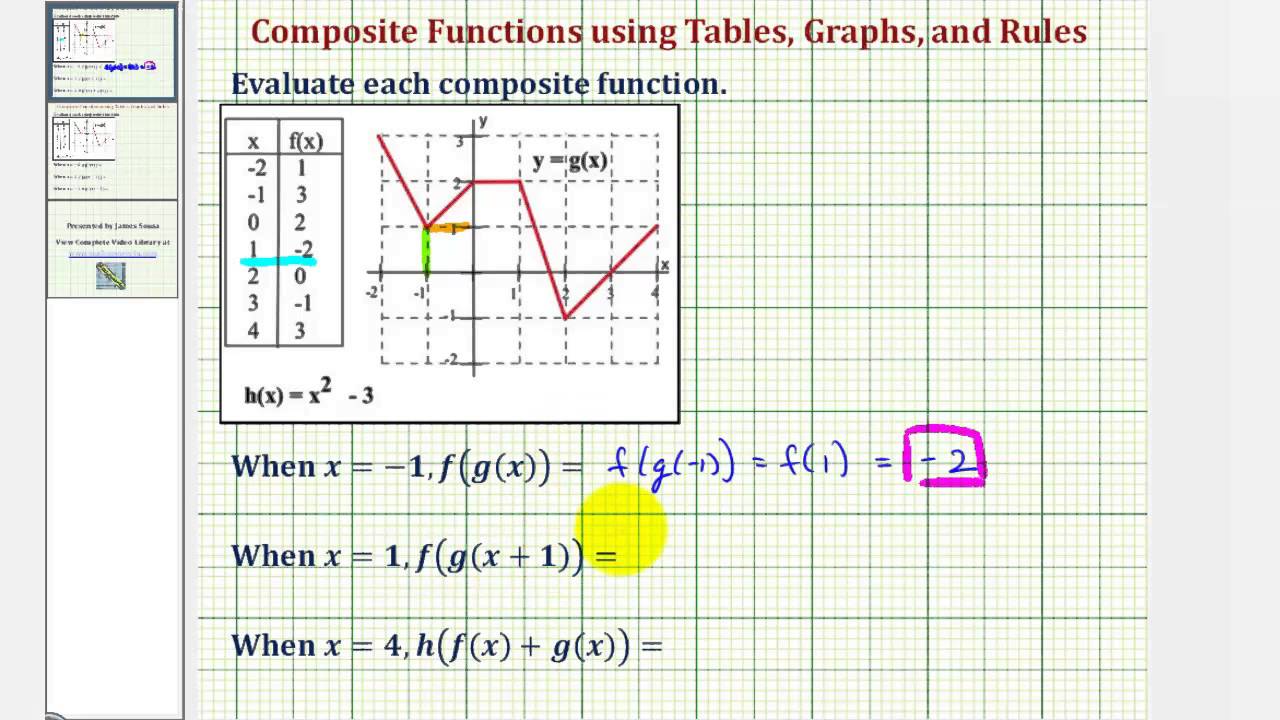
Domain of composite functions rule. As we discussed previously the domain of a composite function such as latex f circ g latex is dependent on the domain of latex g latex and the domain of latex f latex. Such functions are called composite functions. The composite function f g x is read as f of g of x. Let s look at an example where domain restrictions apply.
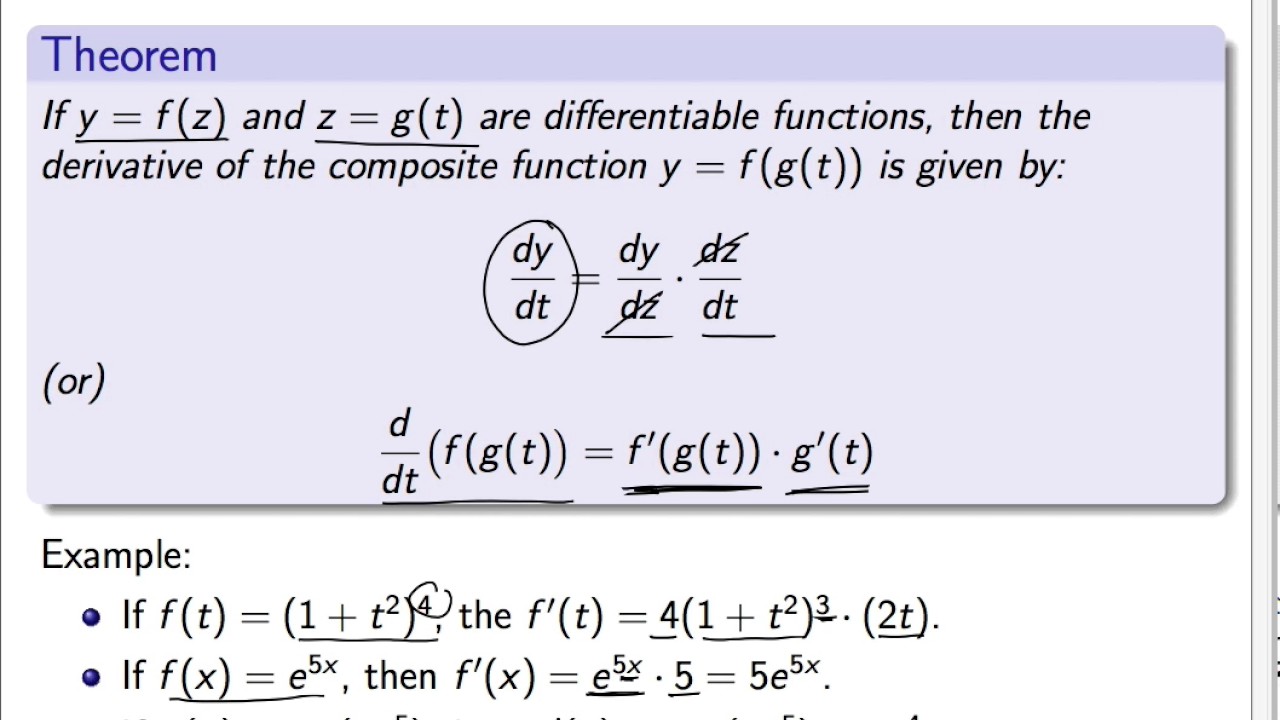
The composite of two functions f x and g x must abide by the domain restrictions of f x and g x. According to the chain rule in layman terms to differentiate a composite function at any point in its domain first differentiate the outer function i e. Chain rule inner and outer functions. The function enclosing some other function and then multiply it with the derivative of the inner function to get the desired differentiation.
Composition of a function is done by substituting one function into another function. It is important to know when we can apply a composite function and when we cannot that is to know the domain of a function such as latex f circ g latex. 1 per month helps. It is important to know when we can apply a composite function and when we cannot that is to know the domain of a function such as latex f circ g latex.
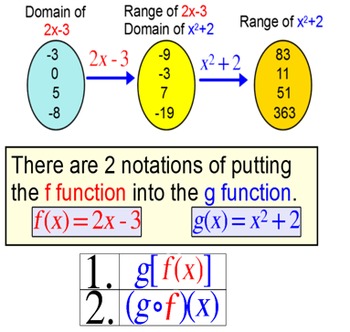
You da real mvps. The function g x is called an inner function and the function f x is called an outer function. For example f g x is the composite function of f x and g x. As we discussed previously the domain of a composite function such as latex f circ g latex is dependent on the domain of latex g latex and the domain of latex f latex.
Let f u sin u. Domain of a composition of fu. Learn how to compose two functions where one or both of those functions is are radical. A composite function is generally a function that is written inside another function.
If we substitute x 2 for u we get the composite function h x f x 2 sin x 2 let f u u 10. If we substitute x 2 1 for u we get the composite function h x f x 2 1 x 2 1 10.