Domain Theory Of Antiferromagnetism
This is like ferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism a manifestation of ordered magnetism.
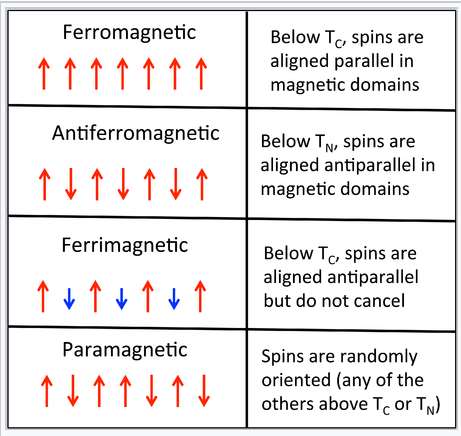
Domain theory of antiferromagnetism. In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules usually related to the spins of electrons align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins on different sublattices pointing in opposite directions. Development of domain theory. Describing antiferromagnetism in density functional theory dft had been an unsolved problem since the 1930s until recently. Ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism ferromagnetism fm exchange interaction heisenberg model spin wave magnon antiferromagnetism afm ferromagnetic domains nanomagnetic particles magnetic order.
1 molecular field theory of antiferromagnetism 2 equal and oppositely directed magnetic sublattices 2 weiss coefficients to represent inter and intra sublattice interactions. The magnetic character of domains comes from the presence of even smaller units called dipoles. According to this theory a single crystal of ferromagnetic solid compresses a large number of small regions and each region is spontaneously magnetized to saturation extent called a domain as shown in fig. H ai n wm a n wm b h hbi nwm a n wm b h magnetization of each sublattice is represented by a brillouin function and each falls to zero at the critical.
Magnetic domain theory was developed by french physicist pierre ernest weiss who in 1906 suggested existence of magnetic domains in ferromagnets. The domain theory of magnetism explains what happens inside materials when magnetized. 7 7 domain theory of ferromagnetism. Antiferromagnetism is the opposite of ferromagnetism where particles align themselves and occurs in materials such as manganese oxide.
He suggested that large number of atomic magnetic moments typically 10 12 10 18 citation needed were aligned parallel. In 1907 weiss proposed domain theory to explain ferromagnetism. Generally antiferromagnetic order may exist at sufficiently low. Antiferromagnetism type of magnetism in solids such as manganese oxide mno in which adjacent ions that behave as tiny magnets in this case manganese ions mn2 spontaneously align themselves at relatively low temperatures into opposite or antiparallel arrangements throughout the material so.
This chapter containing a significant review reports the siwb surrounding or solid coulomb potential induced well for basis set method for the antiferromagnetic state derivation in copper oxides. Chang dept of phys. Antiferromagnetism is when the electrons within a material coalesce forming a chain of oppositely charged particles even though the material as a whole does not appear to have any magnetic quality. Kimichika fukushima in advances in quantum chemistry 2015.
The key difference between ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism is that ferromagnetism can be found in materials having their magnetic domains aligned into the same direction whereas antiferromagnetism can be found in materials in which the magnetic domains are aligned in opposite directions.