Domain Theory Of Ferromagnetic Materials
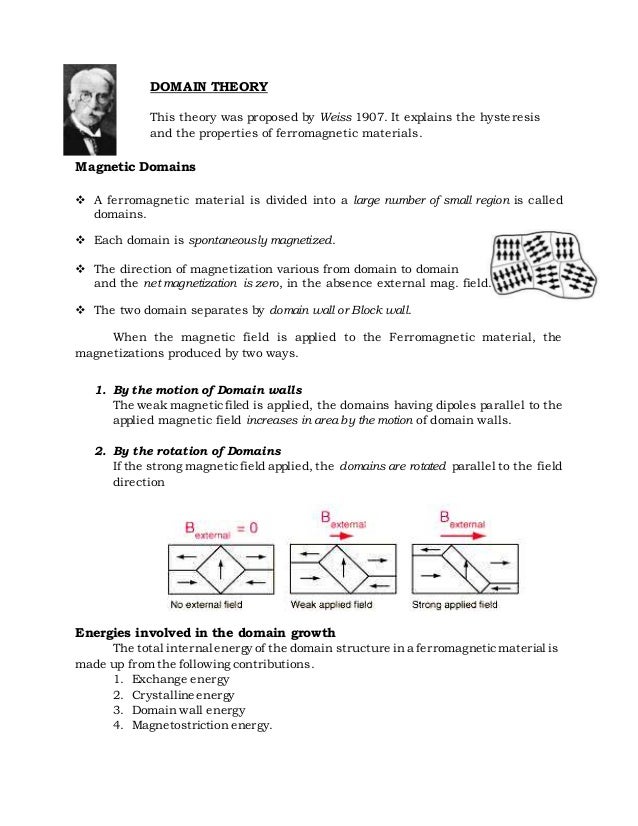
In 1907 weiss proposed domain theory to explain ferromagnetism.
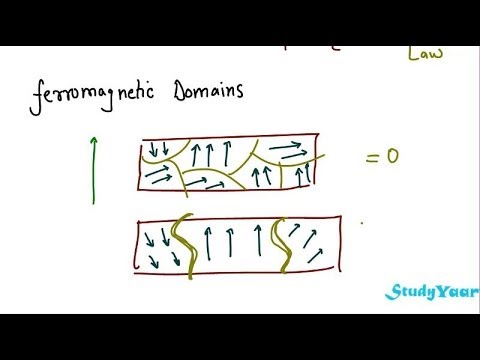
Domain theory of ferromagnetic materials. The magnetization within each domain points in a uniform direction but t. Weiss theory of ferromagnetism is also called domain theory of ferromagnetism. They interact with their neighboring dipoles. According to this theory a single crystal of ferromagnetic solid compresses a large number of small regions and each region is spontaneously magnetized to saturation extent called a domain as shown in fig.
Ferromagnetism is the physical theory which explains how materials become magnets. Weiss theory of ferromagnetism is also called domain theory of. This is based on existing ideas of domain wall motion including both bending and translation. Domain wall a domain wall is a term used in physics which can have one of two distinct but similar meanings in magnetism optics or string theory.
This was later re ned into a theory. This means that the individual magnetic moments of the atoms are aligned with one another and they point in the same direction. Centred tetragonal structure which is ferromagnetic and the ferromagnetism is retained on tempering. Theory of ferromagnetic hysteresis.
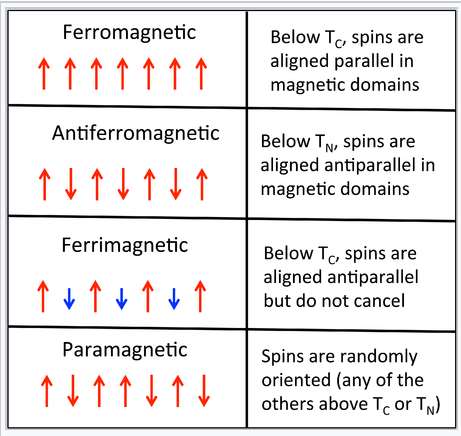
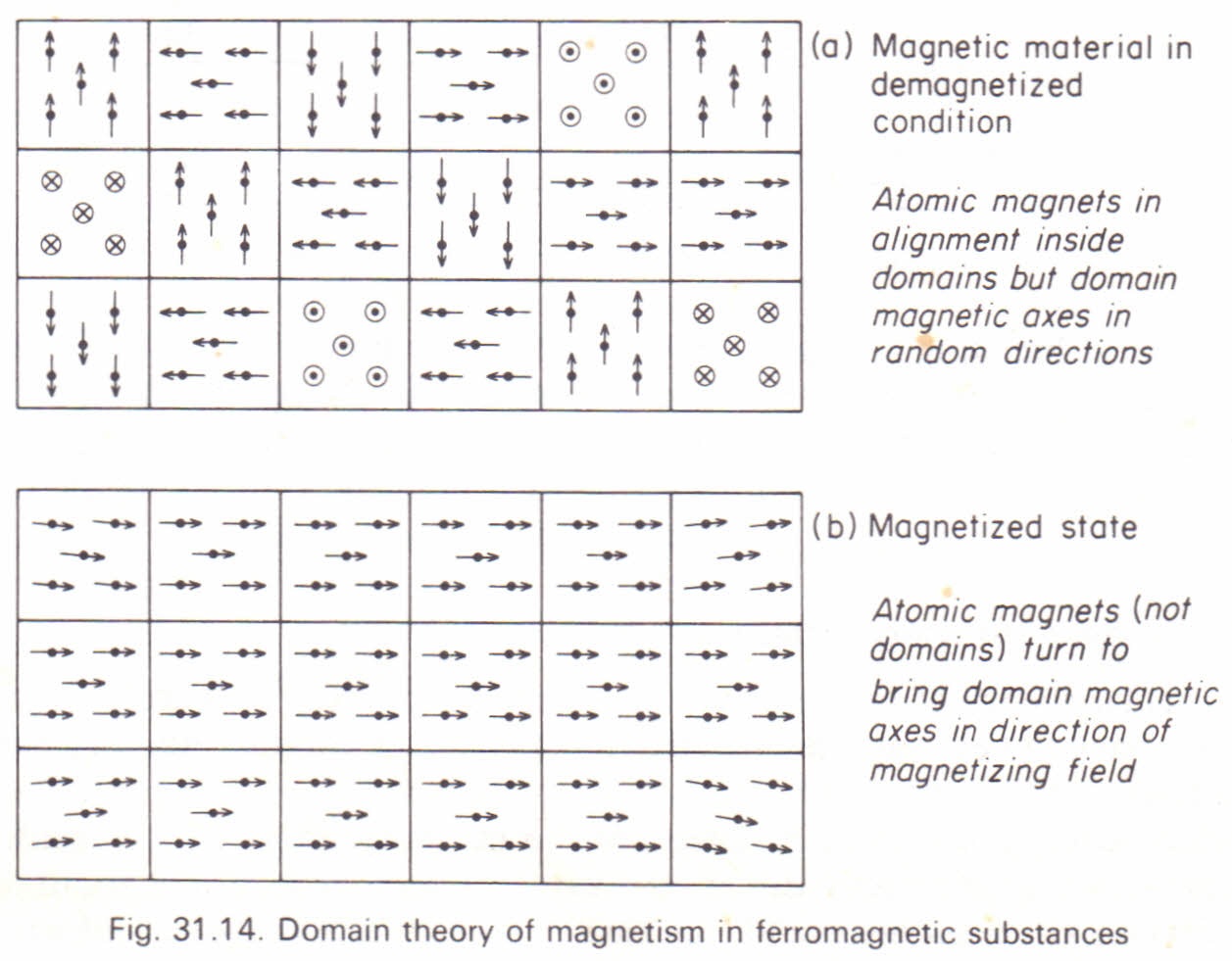
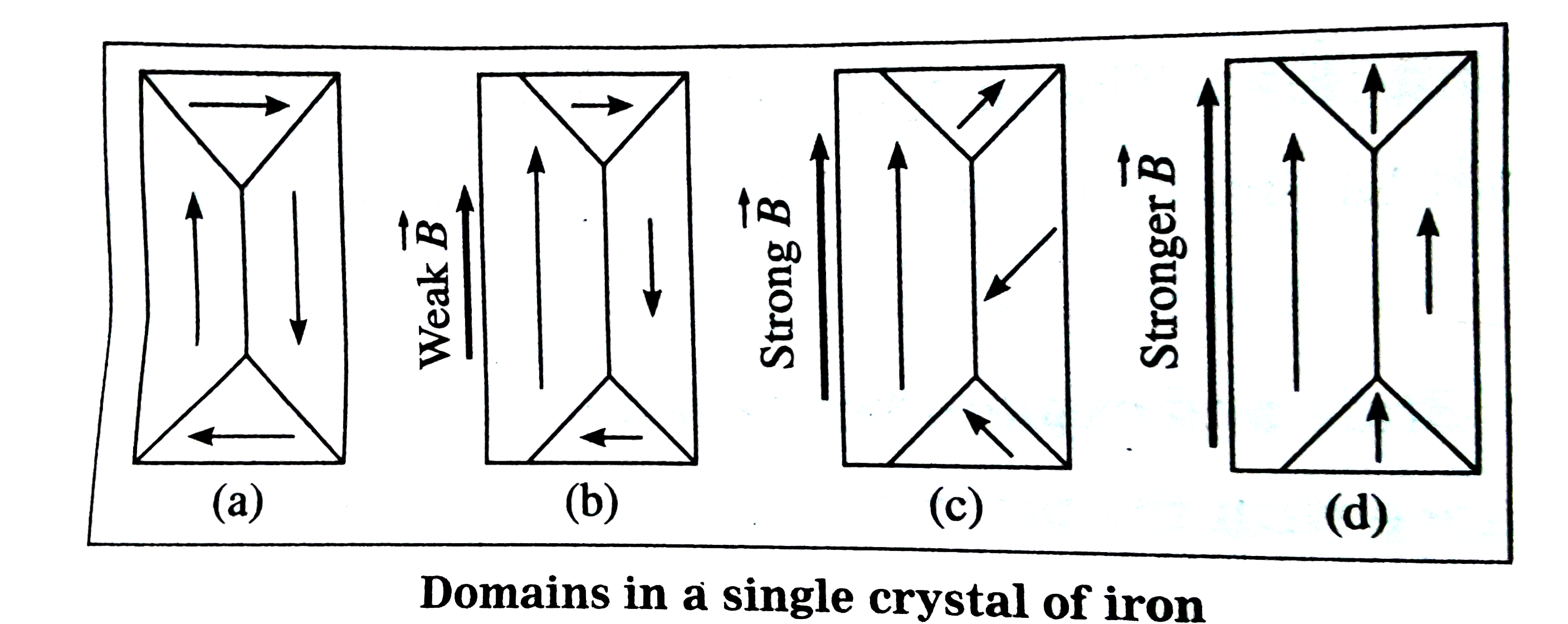
Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials such as iron form permanent magnets or are attracted to magnets in physics several different types of magnetism are distinguished. The domains which are aligned approximately along the direction of the applied magnetic field grow in size at the cost of unfavorably oriented domains that is those align opposite to the field direction get reduced. These phenomena can all be generically described as topological solitons which occur whenever a discrete. It has following points.
A magnetic domain is a region within a magnetic material in which the magnetization is in a uniform direction. He postulated that the neighboring atoms of the ferromagnetic materials due to certain mutual exchange interactions from several number of very small regions called domains. Atoms are arranged in such a way in most materials that the magnetic orientation of one electron cancels out the orientation of another electron. If they align with all the poles in one direction then a larger magnetic domain is produced.
To explain the phenomenon of ferromagnetism weiss proposed a hypothetical concept of ferromagnetic domains. Ferromagnetism along with the similar effect ferrimagnetism is the strongest type and is responsible for the common phenomenon of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Journal of magnetism and magnetic materials. The theory is developed of the domain structure of ferromagnetic bodies whose smallest dimension is comparable with the thickness of the weiss domains as found in crystals of ordinary size.
7 6 the domain size may vary from 10 6 to the entire volume of the crystal. Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which wikipedia. Calculations of the domain boundary magnetic and anisotropy energies of various domain configurations are given for thin films small particles and long needles of ferromagnetic material. However other ferromagnetic substances such as iron are different.
3 1 2 weiss domain theory weiss 1906 1907 postulated that atoms in ferromagnetic materials had permanent magnetic moments which were aligned parallel to one another over extensive regions of a sample.