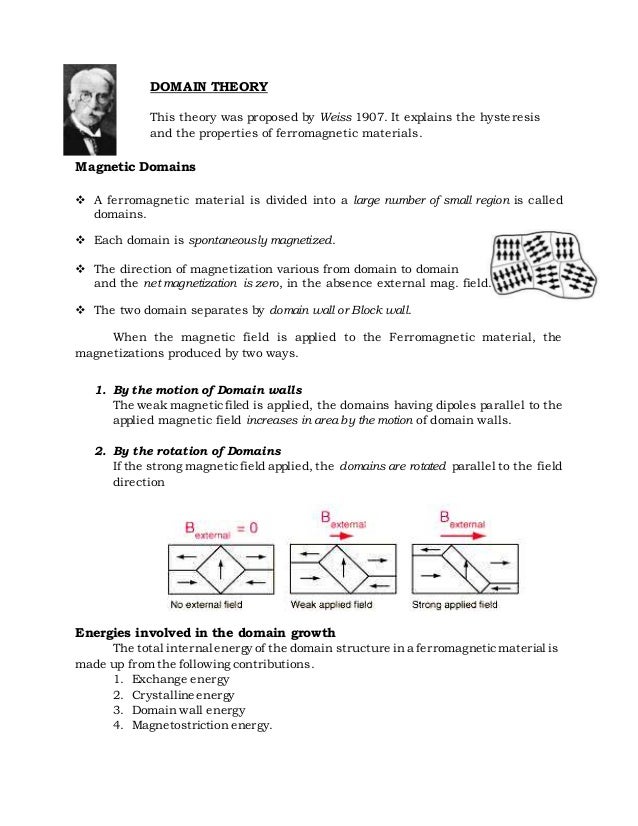
Domain Theory Of Ferromagnetism

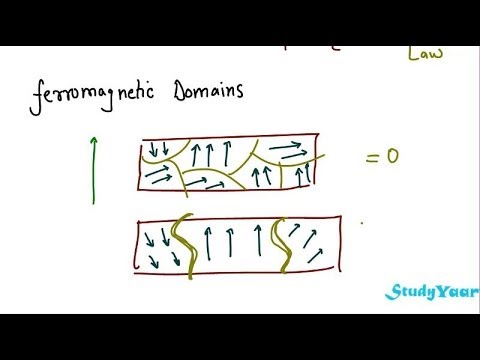
The same specimen may return to the demagnetized state when the external field is removed.
Domain theory of ferromagnetism. Look at other dictionaries. The chapter is organized in two stages. The chapter presents a broad review of the physical principles of domain theory and of the crucial experiments which bear directly on the foundations of the subject of ferromagnetic domains. He suggested that large number of atomic magnetic moments typically 10 12 10 18 citation needed were aligned parallel.
The theory is developed of the domain structure of ferromagnetic bodies whose smallest dimension is comparable with the thickness of the weiss domains as found in crystals of ordinary size. The ferromagnetic material is composed from small. The same specimen may return to the demagnetized state when the external field is wikipedia. Domain theory of ferromagnetism explains 1 two significant observations of materials such as iron.
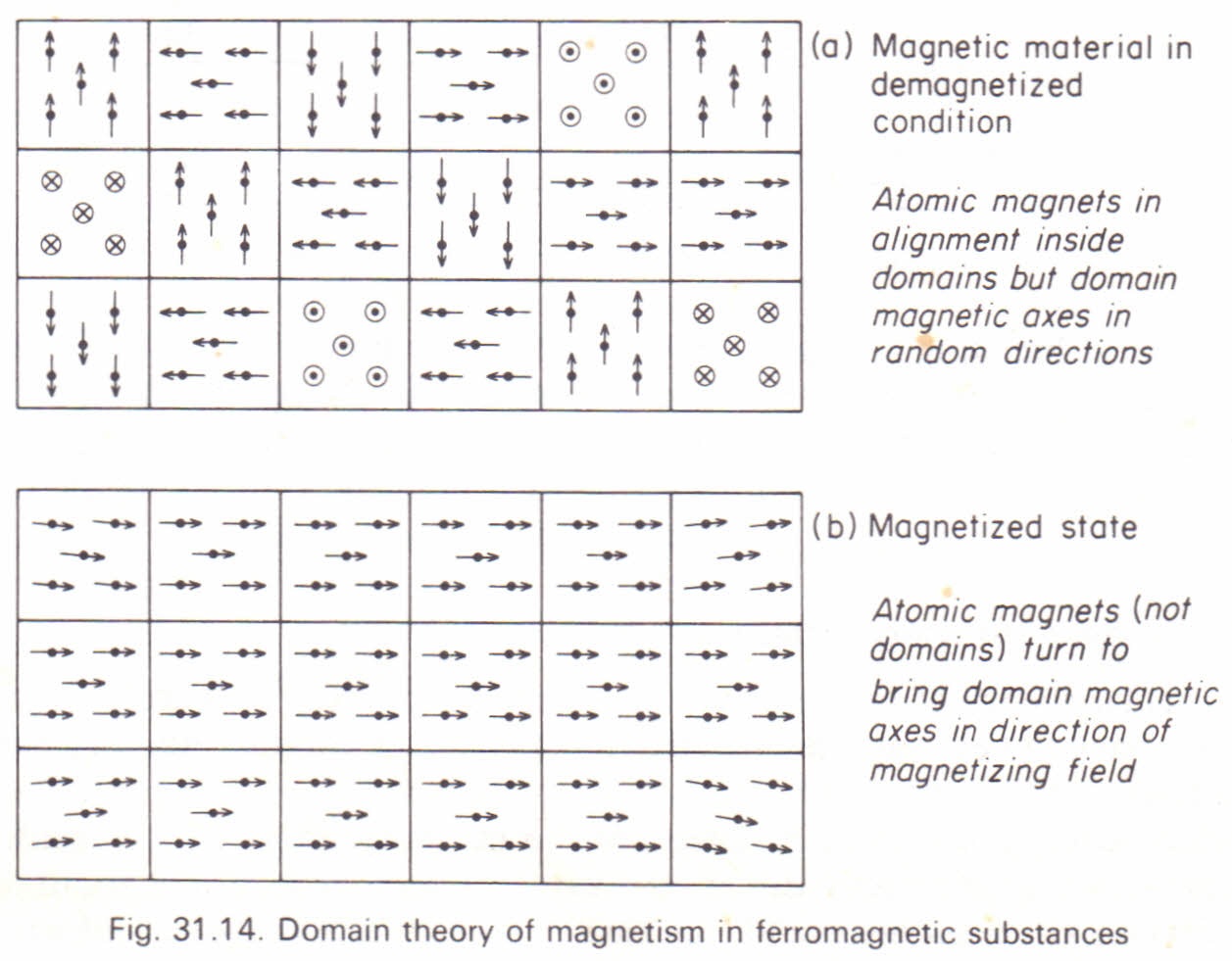
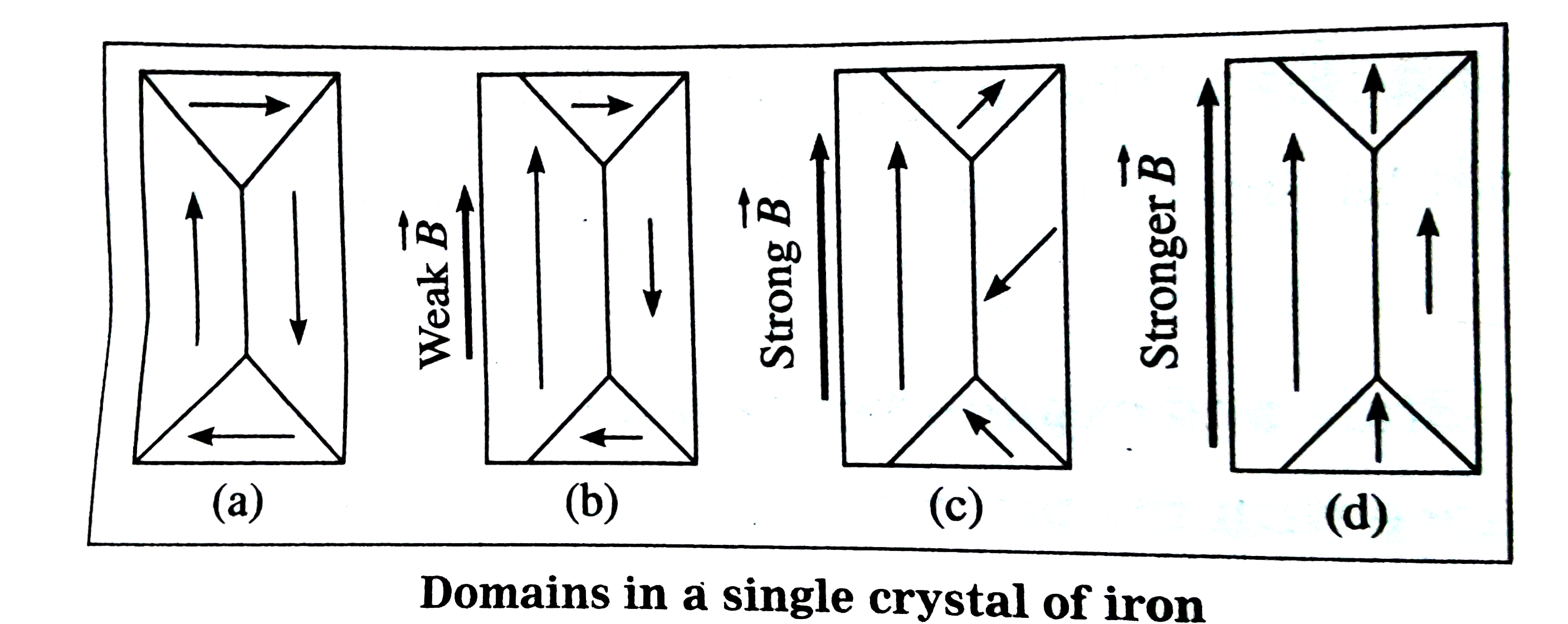
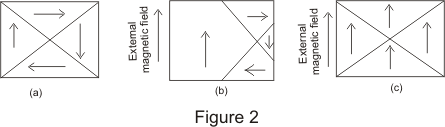
The direction of alignment varies from domain to domain in a more or less random manner. The material may become strongly magnetized by application of a weak external magnetizing field. Domain theory of ferromagnetism explains 1 two significant observations of materials such as iron. Calculations of the domain boundary magnetic and anisotropy energies of various domain configurations are given for thin films small particles and long needles of ferromagnetic material.
All large magnets are made up of smaller magnetic regions or domains. Domain theory of ferromagnetism. Posted on march 26 2011. 2009 10 08 16 22 50 2009 10 08 16 22 50.
In some materials of which iron steel and certain alloys are outstanding examples the atomic magnets or dipoles do not act independently as in paramagnetic substances but small groups interact with one another so that their magnetic axes spontaneously line up together in a certain preferred direction. The magnetic character of domains comes from the presence of even smaller units called dipoles. He postulated that the neighboring atoms of the ferromagnetic materials due to certain mutual exchange interactions from several number of. The domain theory of magnetism.
Magnetic domain theory was developed by french physicist pierre ernest weiss who in 1906 suggested existence of magnetic domains in ferromagnets. The domain theory of ferromagnetism in a paramagnet the increasing magnetisation m is due to the increasing alignment of the magnetic dipoles in the µ b kt magnetic versus thermal competition for a ferromagnet extremely large values of m can be created by the application of very small applied fields h. Domain theory of ferromagnetism. Asked by wiki user.
The chapter presents a study on ferromagnetic domain theory. Development of domain theory. The domain theory of magnetism explains what happens inside materials when magnetized. The material may become strongly magnetized by application of a weak external magnetizing field.