Domain Theory Of Magnetism Ppt

Magnetic domains once domains form the orientation of magnetization in each domain and the domain size are determined by magnetostatic energy crystal anisotropy magnetoelastic energy domain wall energy 15.
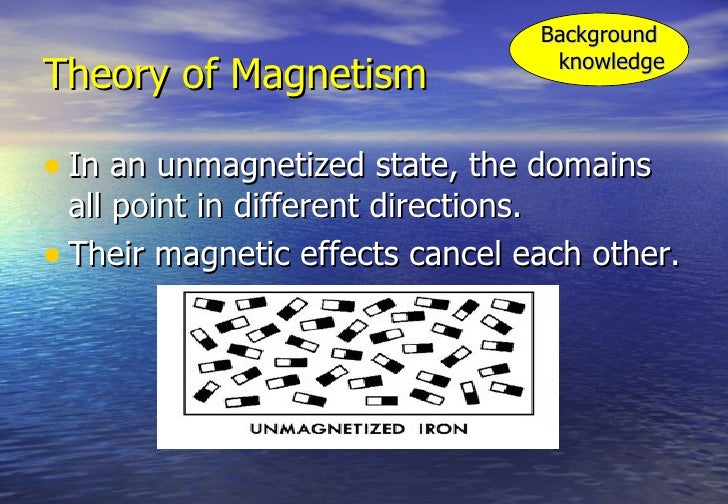
Domain theory of magnetism ppt. The domain theory of ferromagnetism. The overall magnetisation magnetic moment per unit volume of a block of material is the vector sum of the domain magnetisations. All large magnets are made up of smaller magnetic regions or domains. Domain formation in a saturated magnetic material is driven by the magnetostatic ms energy of the single domain state a.
Illustration bellow shows how formation of domains yields to zero net magnetization b c in the absence of external magnetic field. The black bars represent the range of grain sizes sizes for which that number of domains is the lowest energy domain state. The magnetic character of domains comes from the presence of even smaller units called dipoles. A theory of magnetism.
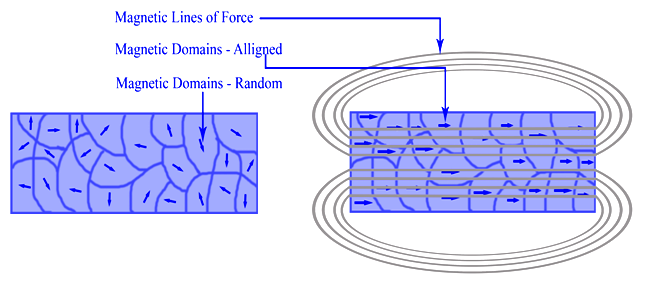
The magnitude of the magnetism m of a sample is equal to the vector sum of the magnetisation of the domains the regions of spontaneous magnetisation obviously already exist and the external field h. What is the theory of magnets. As a eld is applied changes in the domain con guration for example in the. The same specimen may return to the demagnetized state when the external field is removed.
The material may become strongly magnetized by application of a weak external magnetizing field. Covers magnetic materials domains attraction an repulsion magnetic fields compasses and how to make a compass. Domain theory of ferromagnetism explains 1 two significant observations of materials such as iron. A theory of magnetism.
If a piece of magnet is dropped broken into 2 or more pieces each piece is noticed to behave just like the original magnet. It is able to exhibit all the properties of a magnet. Domain theory of magnetism. In the demagnetised state this is zero.
Magnets have a north and south pole n s all magnets are made of many smaller magnets called. After moon merrill 1985 van der voo 1990 9. This was later re ned into a theory of domains of parallel moments weiss 1926. The domain theory of magnetism explains what happens inside materials when magnetized.
In this case each domain is magnetized to saturation in the direction of one of the easy axes but the sum of the domain magnetization is zero. If each piece of magnet is again dropped broken.