Domain Trust Authentication Process

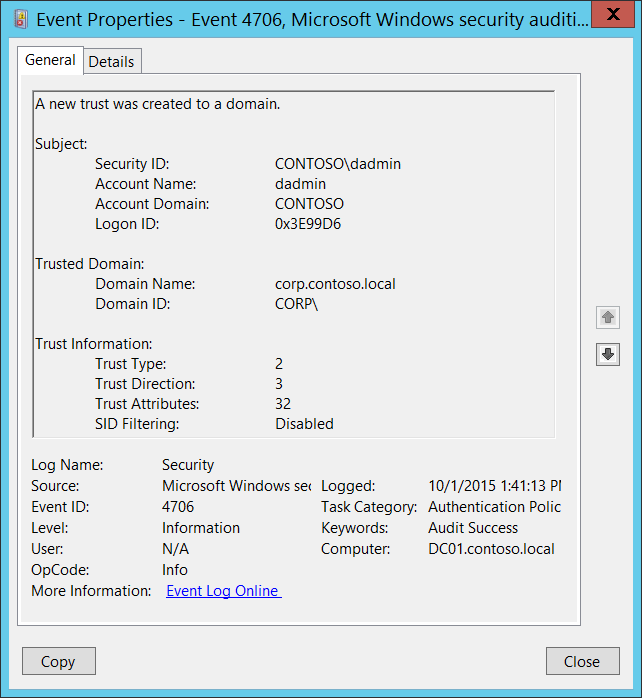
When a new tree is added to a domain ad applies a tree root trust.
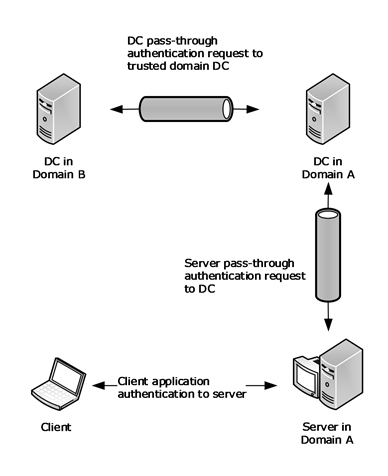
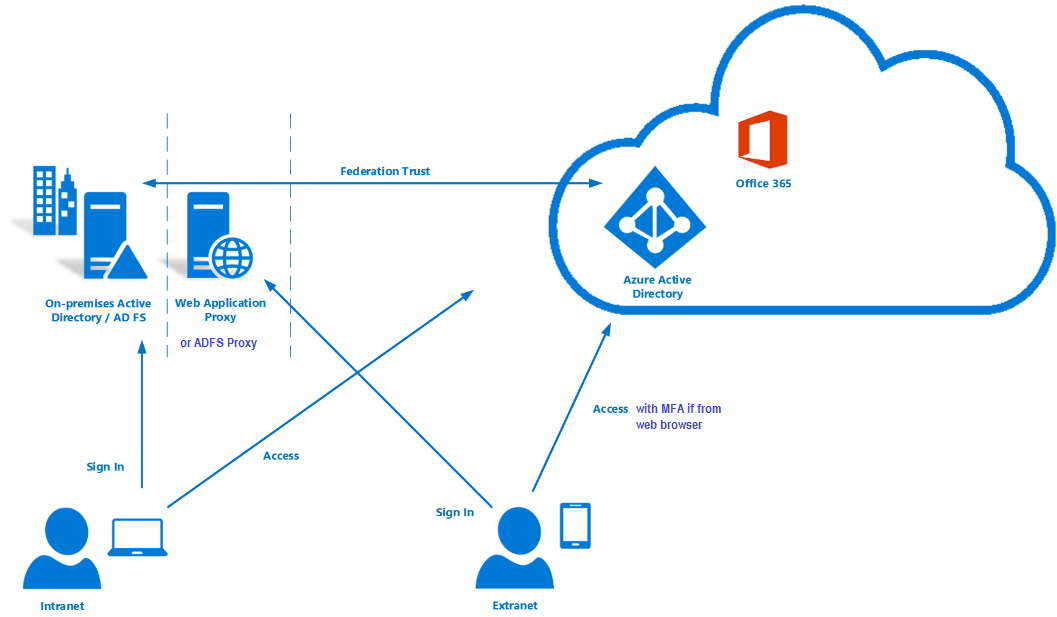
Domain trust authentication process. The following kerberos v5 authentication process occurs. To make such scenarios work the domain of the server called the resource domain and the domain of the user account called the account domain engage in a trust relationship in which authentication decisions made in the account domain are trusted in the resource domain. A realm trust enables you to create a trust between a non windows kerberos realm and a windows server domain. This process can take too long at times.
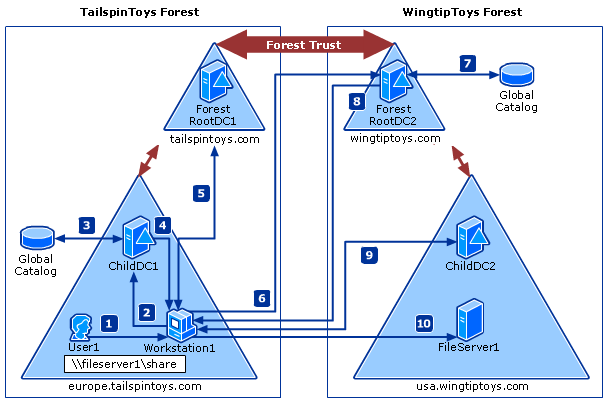
Hi rob your issue seems to be ntfs permissions rather then the usual authentication issue if you re 2 way trust is functioning correctly. In a complex forest this can take time which you can reduce with shortcut trusts. The trust path is the series of domain trust relationships that the authentication process must traverse between two domains in a forest that are not directly trusted by each other. What you should do is create a global security group in the domain in which your iis or file server hosting the content of the web site is located.
This ticket is required for user1 to be authenticated to resources. The direction of the trust and whether the trust is transitive or nontransitive must also be determined before it authenticates the user to access resources in the domain. In such trust relationships the resource domain is called the trusting domain while the account domain is called the trusted domain. When a trust exists between two domains the authentication mechanisms for each domain rely on the validity of the authentications coming from the other domain.
As part of the logon process the authenticating domain controller issues the user a ticket granting ticket tgt. Shortcut trusts are one way or two way transitive trusts that administrators can use to optimize the authentication process. Before authentication for a user computer or service can occur across trusts windows must determine if the domain being requested has a trust relationship with the requesting account s logon domain. Authentication request must first travel a trust path between domain trees.
When a request for authentication is referred to a domain the domain controller in that domain must determine whether a trust relationship exists with the domain from which the request comes. In that security group add all the users from the first domain that would have access to the web sites. Trusts help to provide controlled access to shared resources in a resource domain the trusting domain by verifying that incoming authentication requests come from a trusted authority the trusted domain. Realm trusts can be one way or two way transitive or non transitive.